
Heavy plate handling in industries such as construction, metallurgy, and ports is fraught with potential safety hazards. Common safety accidents include plate slippage, uneven loading, and operator errors. Slippage can occur due to improper clamping or wear of the clamping surface, leading to the sudden release of the plate during lifting. Uneven loading, caused by misaligned placement of the plate on the clamp, can result in excessive stress on one side, increasing the risk of structural failure. Operator errors, such as incorrect operation of the lifting equipment or failure to follow safety procedures, are also significant factors contributing to accidents.
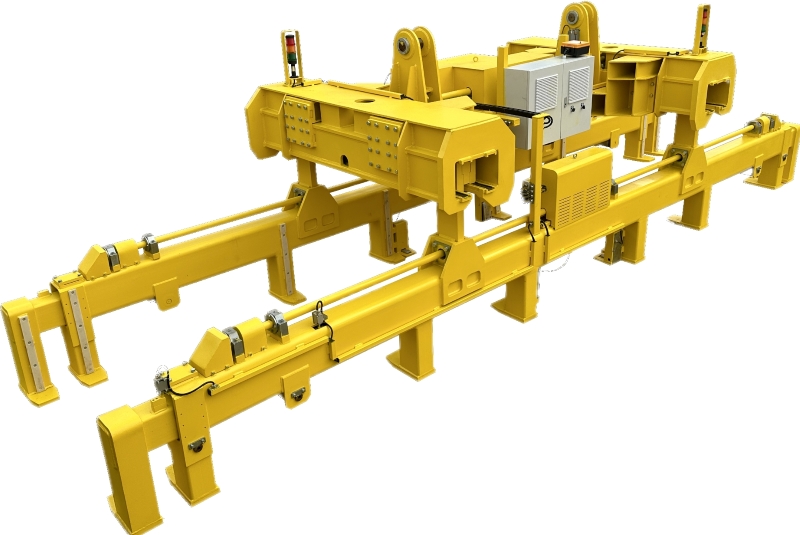
Dalian Tiding Heavy Industry's high - strength alloy steel slab clamps are equipped with built - in limit switches and multiple safety redundancy designs. The limit switches are strategically placed to detect the position and status of the clamp. For example, they can sense when the clamp has fully engaged with the plate, ensuring a secure grip. The multiple safety redundancy design includes additional backup mechanisms to prevent failures in case the primary safety system malfunctions. This active prevention and control mechanism significantly reduces the risk of accidents by detecting and correcting potential problems before they occur.
There are differences in safety performance among hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical driving modes. Hydraulic - driven clamps generally offer better safety performance compared to mechanical or pneumatic ones. Hydraulic systems provide more precise control, better shock absorption, and higher reliability. They can quickly respond to changes in load and adjust the clamping force accordingly, reducing the risk of slippage and overload. In contrast, mechanical and pneumatic systems may be more prone to wear and tear, and their control accuracy is relatively lower.
| Driving Mode | Safety Performance |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic | High - precision control, good shock absorption, low accident rate |
| Mechanical | Prone to wear, relatively lower control accuracy |
| Pneumatic | Susceptible to air leakage, less reliable in some cases |
Overseas project cases demonstrate the effectiveness of the limit switch and safety redundancy design in complex working conditions. For instance, in a large - scale port project, the clamps were used to handle heavy steel plates in high - wind and high - humidity environments. Despite the challenging conditions, the clamps with the advanced safety design successfully completed the handling tasks without any major accidents. The limit switches accurately detected the position of the plates, and the safety redundancy mechanisms ensured continuous operation even when faced with minor malfunctions.
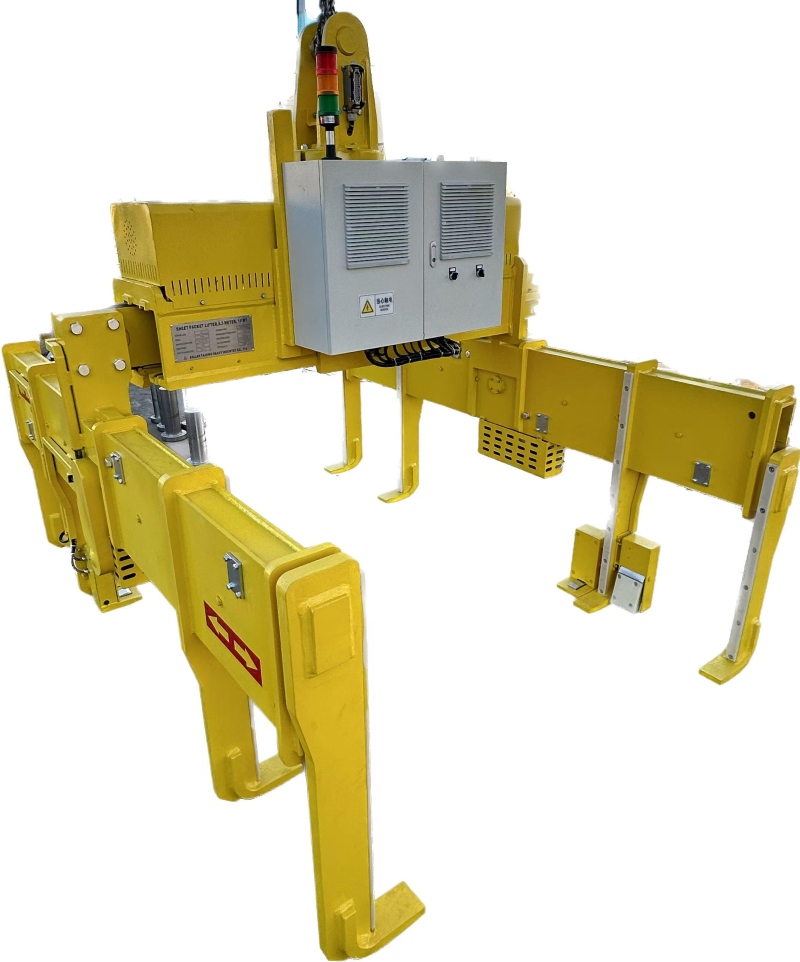

Feedback from on - site operators shows a significant reduction in accident rates. In some projects, after the installation of the high - strength alloy steel slab clamps with the advanced safety design, the accident rate decreased by up to 60%. Operators reported that the clamps were easier to operate, and they felt more confident in handling heavy plates. The improved safety features also led to increased work efficiency as less time was spent on dealing with accidents and potential hazards.
When selecting equipment, procurement decision - makers should prioritize the following safety functions: built - in limit switches, multiple safety redundancy designs, reliable anti - slip and anti - overload protection mechanisms, and compatibility with different driving modes. By considering these factors, they can choose the most suitable clamps to improve the safety and efficiency of plate handling operations.

In conclusion, safety is the key to efficiency in plate handling. Dalian Tiding Heavy Industry's high - strength alloy steel slab clamps offer a reliable solution to reduce the risk of accidents. If you are interested in learning more about how to improve the safety of your plate handling operations, click here for more information.
Do you have any problems with plate handling? Share your experiences in the comments below!

